Rammed Earth Tiny House Rethinks Farmhouses With Green Solar Roof
We have seen many building designs combining ancient building techniques with sustainable energy technology. Keeping up with this ongoing trend, the Rammed Earth House in Slovenia boasts a unique style farmhouses. It showcases a simple way to merge traditional rammed earth building methods along with modern solar energy production. This reinterprets the early 20th-century farmhouse design in the modern world. The resulting tiny house boasts unique angles and a multi-angled pitched roof. Furthermore, the tiny home orients maximum sun exposure, as well as passive solar heating with windows kept for proper cross-ventilation in warm weather.
Tiny house combines traditional building methods with modern techniques
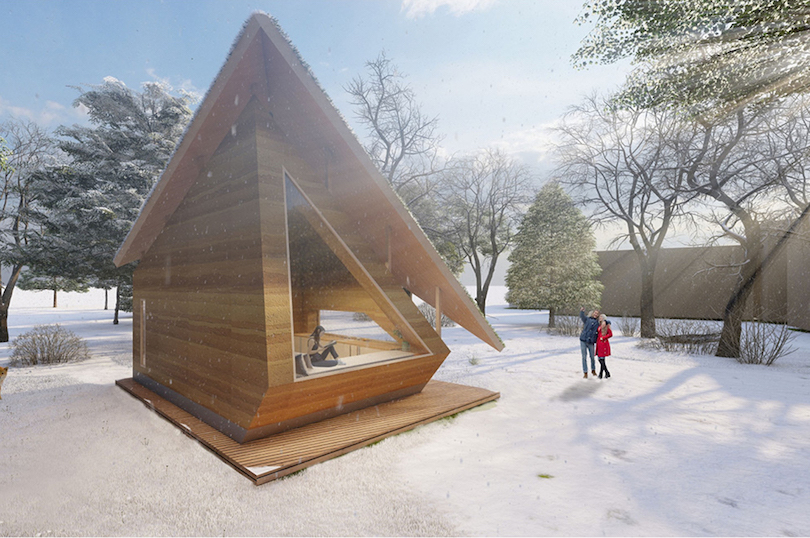

The green roof boasts grass and solar panels to power the house. The tiny house also boasts a rainwater collection system for facilitating proper water recycling. Dating back to the 9th-7th millennium BC, the rammed earth building technique is one of the most reliable methods for home structures. This building method is suitable for almost every continent except Antarctica. Now, the three architects Aslı Erdem, Merve nur Başer, and Fatma Zeyneb Önsiper have brought the method to Slovenia. The architects have conceptualized their tiny home to combine traditional building methods with modern solar energy production methods.
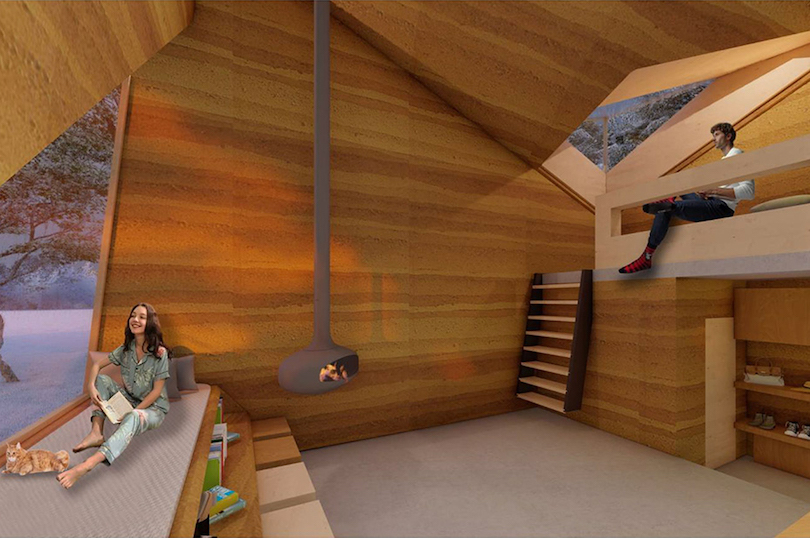

For conceptualizing the sustainable tiny house, the architects’ team also set out for balancing contemporary energy production techniques along with age-old building practices. Situated in Dobrava, a small settlement in the flatland region of Slovenia, this tiny house has taken a cue from the popular floating roof created by Oton Jugovec, a Slovenian architect.
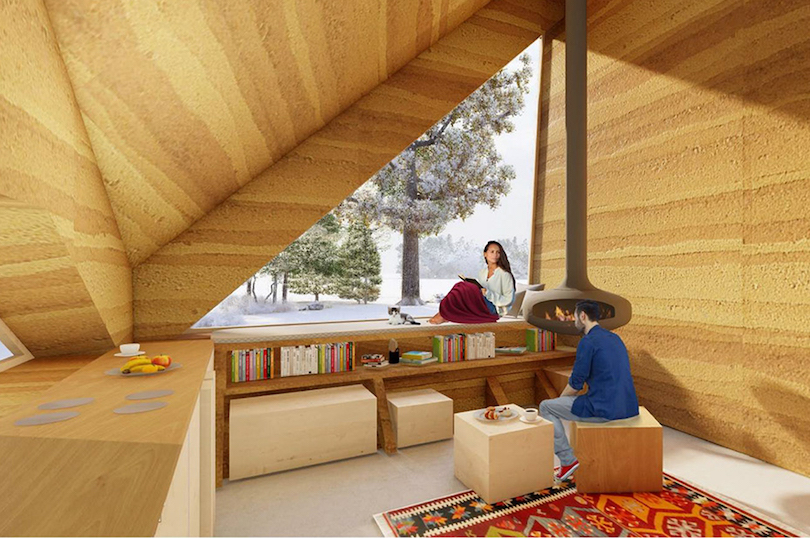

Since rammed earth consists of a technique to compact a subsoil mixture into a well-supported framework, the three architects beautifully conceptualized a concrete foundation with a timber framework. It is not easy to bring changes to any rammed earth structure. However, the house’s overhanging roof enables the cement addition to provide extra stability to the given structure. Furthermore, this house comes sheltered with an overhang green roof, which works well to protect the building material from erosion threats. It is because the region of Dobrava often experiences temperature, rainy, and snowy seasons.
Sustainable passive heating and insulation methods
The sustainable build of this tiny home also enables passive insulation. Meanwhile, the heating techniques warm-up and cool off the building. Specifically created to bring in the sun rays indoors during the winter months and block them during the hotter season, the tiny house is influenced by the surrounding environment. Even the climate of the region ensures comfortable, insulation, and passive heating all year round.
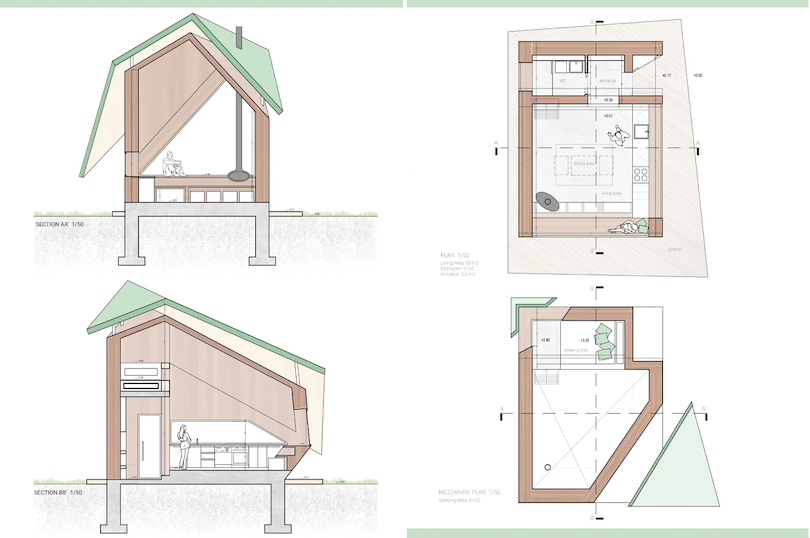
You can have a look at the images to see how the windows are arranged strategically for enabling cross-ventilation within the house. Even the green roof holds various photovoltaic panels for powering this home with the production of solar energy. Meanwhile, the rainwater collector helps in water recycling and comes integrated with a septic tank system. Even the living area is well-suited to enjoy the benefits of insulation and passive heating methods. For instance, the north facade boasts fewer windows than the west facade. Due to this design, there is a decrease in potential heat loss in the winter season.
Via: Inhabitat
